Courses

 Compare
Compare
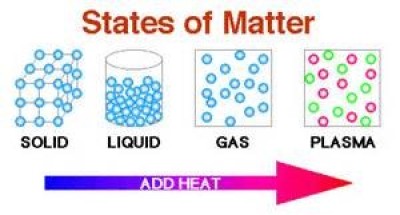
Solid, liquid, gaseous and plasma are the four states for a given substance that can exist (Fig. 1). The chemical composition of the substance is the same in solid, liquid, and gaseous states. Properties of matter that can be changed with changing the state of a substance: density, elasticity, surface tension, viscosity, specific heat, conductivity, semi-conductivity, Ferro-magnetism, Para magnetism, reflecting properties of light etc.
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
It is a property of a matter for which a material body able to regain its initial state of condition on removal of the external forces that applied on it.
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
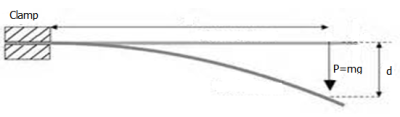
A rod or a bar of uniform cross-section, circular or rectangular, the length of which is very much greater than its thickness is called a beam. When at the one end of a fixed beam is loaded, it bends due to the moment of the applied force (Fig. 15).
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
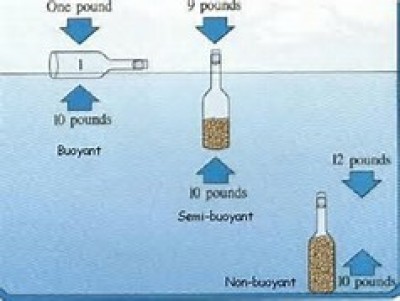
At rest the properties of fluids can be described by the concepts of pressure and density, by Archimedes’ principle of buoyancy and by Pascal’s law of transmission of pressure (Fig. 1).
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
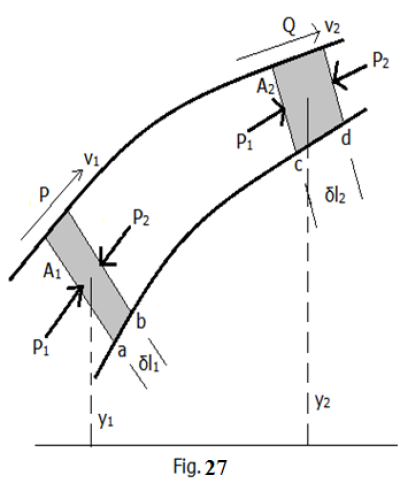
Consider a steady, incompressible, and non-viscous fluid flowing through a portion of a tube of flow as shown in Fig. 8. Let y1, v1 and A1 be the elevation, velocity of the fluid and area of cross-section of the tube respectively at the first point P and y2, v2 and A2 be the corresponding values at the second point Q. There are two forces that work on the shaded element of the liquid to raise the element from one point (say P) to another (say Q). These are (i) the force due to pressure and (ii) the force due to gravity. Moreover, the amount of fluid remaining unchanged in the two positions.
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
What is light and how the light energy is propagated through space (i.e., the nature of light) are discussed in Physical Optics.
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
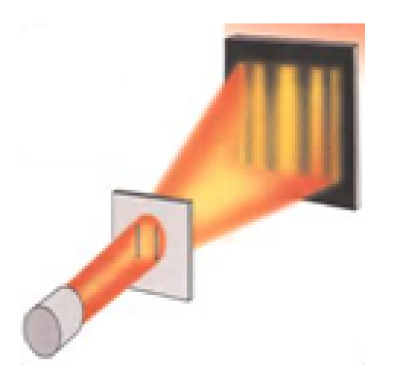
The modification of light intensity due to superposition of two or more beams of light is known as interference of light. The interference is said to be constructive or destructive when the resultant intensity is
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
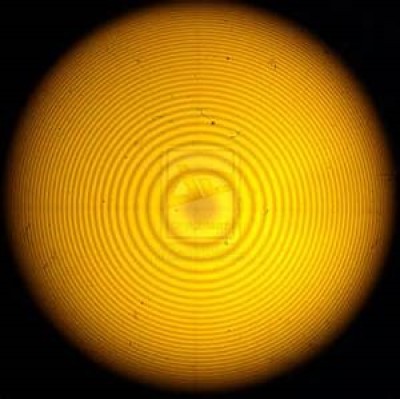
To produce Newton’s rings a plano-convex lens of large radius of curvature is placed on a glass plate so that its convex surface faces the plate, a thin air film of progressively increasing thickness in all directions from the point of contact between the lens and the glass plate is very easily formed
0 Lessons
Hours

 Compare
Compare
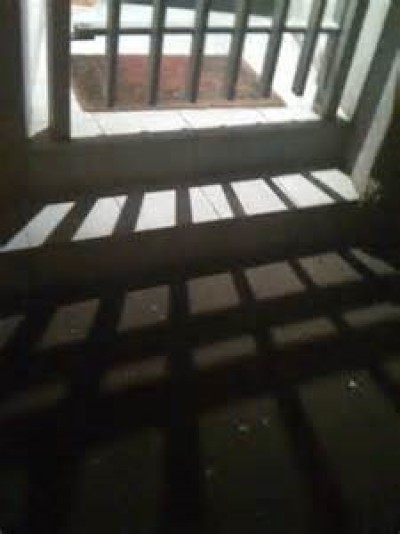
Diffraction is the slight bending of light as it passes around the edge of an object (Fig. 26). In the atmosphere, diffracted light is actually bent around atmospheric particles - most commonly, the atmospheric particles are tiny water droplets found in clouds
0 Lessons
Hours