Courses


 Compare
Compare
A particle may be simultaneously acted upon by more than one simple harmonic vibrations acting either along the same straight line or at right angles to each other. The resultant displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc., of the particle is given by the vector sum of the corresponding quantities due to the individual waves. Combination of two simple harmonic vibrations of same frequency but different phase and amplitude: Let a particle in a medium be simultaneously acted upon by two simple harmonic vibrations of same frequency but different phase and amplitude given by the following equations,
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
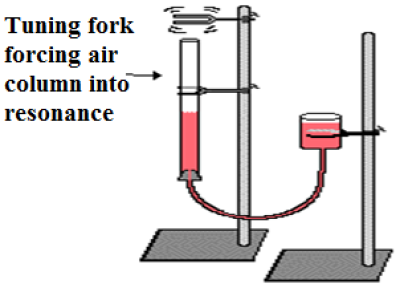
The bob of a simple pendulum (Fig. 7 a) executes simple harmonic motion and if there is no loss of energy by friction or otherwise, the pendulum will go on oscillating with the same time period and amplitude for any interval of time. These types of vibrations are referred to as undamped free vibration (Fig. 7 b).
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
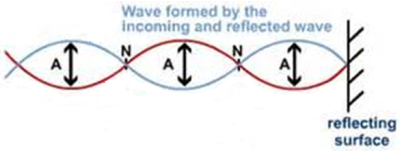
Wave motion can be thought of as the transport of energy and momentum from one point in space to another point without the transport of matter (Fig. 10 a). Water waves, sound waves, light waves and radio waves are the examples to carry
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
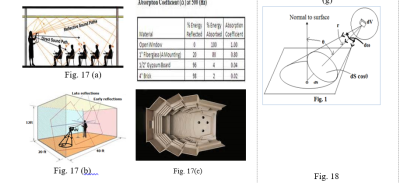
Acoustics is the branch of physics that deals with the process of generation, reception and propagation of sound. This branch of physics is closely related to various branches of engineering. For example, architectural acoustics, which is dealing with the design and construction of buildings, recording studios, television broadcasting stations, music halls, operas, etc. (Fig. 17 a, b, c, d).
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
If a nucleus be too heavy or has excess energy, and not has the right balance of protons and neutrons then it will be a unstable nucleus. To be stable it will emit radiation (particles of matter and rays of energy, Fig. 1a), and in so doing becomes nucleus of other elements (Fig. 1b). The process of emitting radiation is called radioactivity. Despite the strength of the forces that hold nucleons together to
0 Lessons
Hours

 Compare
Compare
The number of atoms disintegrated per second at any instant is directly proportional to the number of radioactive atoms actually present in the sample at that instant. Therefore, the rate of disintegration is governed by an exponential law. Moreover, it implies that the number of atoms that break up at any instant is not affected by environmental factors (like temperature, pressure, chemical combination, etc.)
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
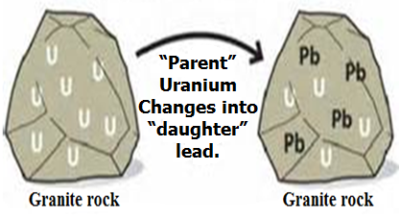
It is a condition established in a parent/daughter mixture when both parent and daughter are radioactive and when the daughter’s half-life is shorter than that of the parent. If the daughter’s half-life exceeds that of the parent, equilibrium will never be reached.
0 Lessons
Hours

 Compare
Compare
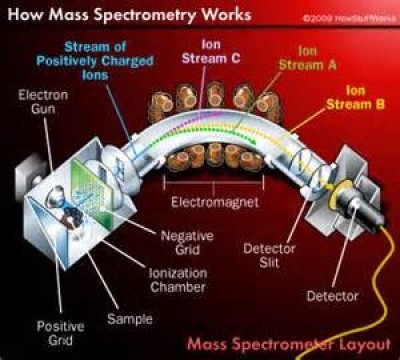
Nuclei are made up of protons and neutrons. Let Zmp and Nmn be the individual masses of Z protons and N neutrons and which are combined to form a nucleus. Accurate measurement of nuclear masses by mass spectrometers (Fig. 10 a) show that the actual mass of a nucleus, containing Z protons and N neutrons
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
When two nuclei come close together, or else a nucleus of an atom and a subatomic particle (such as a proton, neutron, or high energy electron) from outside the atom, collide, a nuclear reaction can occur to produce one or more nuclides that are different from the nuclide(s) that began the process. Therefore, nuclear reaction is a process in which the structure and energy content of an atomic nucleus are changed by interaction with another nucleus or particle
0 Lessons
Hours