Course description
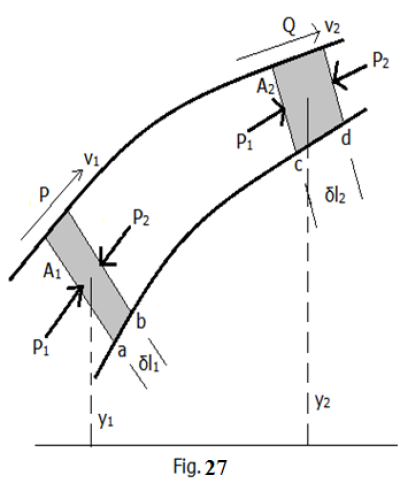
Since the fluid is under pressure at all points, inwards forces due to P1 and P2 are exerted against both faces of the element.
If A represents the cross-sectional area of the tube at any point and P represents the corresponding pressure, then the force, F = PA.
The work done by the force acting on the left face of the element in motion is
The above equation is referred to as Bernoulli’s theorem (or equation) and may be stated as follows:
For streamline motion of an incompressible non-viscous fluid, the sum of the pressure at any part plus the potential energy per unit volume plus the kinetic energy per unit volume there is always constant.
Ø For the special case when the flow of the fluid is horizontal, the height y is constant then Bernoulli’s equation reduces to
Problem 1: Water in a horizontal pipe of a non-uniform bore flows with a velocity of 40 cm/sec at a point where the pressure is 2 cm of mercury column. What is the pressure at a point where the velocity of flow is 60 cm/sce? Given that g=980 cm/sec2 and density of water = 1 gm/cc.
Experimentally it is showed by Osborne Reynolds that the critical velocity vc for a liquid is = ; where ρ and ɳ are the density and coefficient of viscosity of the liquid respectively, r is the radius of the tube and k is number, called Reynolds number. The value of k is very high and is, therefore, usually represented on a logarithmic scale.
For narrow circular tubes the motion will be streamline when k < 1000. The motion becomes turbulent when k exceeds 2000
Coefficient of viscosity of the liquid, ɳ = (F⁄A)/θ=(F⁄A)/(v⁄l)
(Fig. 9)
Flow of liquids
Q1. Show that the rate of flow of liquid is
Q2. Explain the terms Streamline, Turbulent and Laminar flow.
Q3. Derive an expression for the equation of continuity.
Q4. Derive Bernoulli’s equation for a fluid in streamline motion.
Q5. What is Reynold’s number? Explain the significance of the Reynold’s number.