Courses


 Compare
Compare
Environmental science is the systematic study of our environment- natural and human, and our proper place in it. Since the conditions of both worlds affect individual and community, they are essential to our lives, and constitute important components of the environment. It is essentially an inter-disciplinary approach that brings about an appreciation of changes in our natural and built environment. As an applied science, it seeks to provide answers- practical solutions, to the complex problems of how to make human civilization sustainable within the carrying capacity of the global ecosystems. This is why, it is not just a mere collection of facts about the environment;
0 Lessons
Hours

 Compare
Compare
Our planet Earth may be viewed as a complex environmental system consisting of different interacting sub-systems or components. Here, a steady influx of solar radiation provides the heat and light energy needed to support life in the biosphere. This chapter characterizes the basic structures of these life support (bio-physical) sub-systems i.e. atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere and biosphere including an overview of their functions and inter-connectedness.
0 Lessons
Hours

 Compare
Compare
An ecosystem is a biotic assemblage or grouping of organisms taken together with their environment. It is a region with a specific and recognizable landscape form. The nature of the biotic grouping in the region is based on its geographical features. There are various kinds of life supporting systems that are found on the surface of the Earth, such as hills, mountains, plains, forests, grasslands, deserts, wetlands, oceans, coastal areas, islands, lakes, rivers, and estuaries.
0 Lessons
Hours

 Compare
Compare
Natural resources and ecosystem management involves managing whole geographic landscape over long time, taking human needs into consideration, maintaining biodiversity and ecological processes, utilizing innovative institutional arrangements, integrating economics, science and policy, encouraging public involvement, and adapting management based on conscious experimentation and routine monitoring. Ecosystem management, like sustainable development, recognizes that societal goals, environmental quality, and economic health are all inextricably interlinked. Natural resources management is fundamentally concerned with ecosystems interactions- of energy, air, water, mineral, plant, animal and microbial components. A key concept here is that any human activity influencing one
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
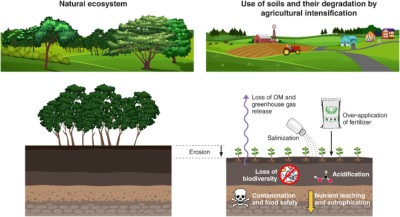
Agro-ecosystems are biological and natural resource systems managed by humans for the primary purpose of producing food as well as other socially valuable nonfood goods and environmental services. These are contained within larger landscapes, which include uncultivated land, drainage networks, rural communities, and wildlife. Agro-ecosystems cover more than one-quarter of the global land area, but almost three-quarters of the land has poor soil fertility, and about one-half has steep terrain, constraining production. A further limitation is the growing competition from other forms of land use such as urban, industrial
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
Water is the most vital element among the natural resources, and is crucial for our very existence. Without water, life as we know it could not exist. All living organisms including man, all the life supporting process of the earth system is heavily dependent on water. Living cells themselves consist mainly of water. The human body is two-thirds water- an essential nutrient in every function. It helps transport other nutrients and waste products in and out of cells. Water dissolves the carbon dioxide, oxygen and salts present in the body and distribute to the different parts through the process of blood circulation. It is greatly needed for the maintenance of proper body temperature.
0 Lessons
Hours

 Compare
Compare
Energy is the mode of life. It is essential for most human activities in modern society, and is the prime engine for economic growth and technological development. As an index of civilization, it generally correlates with standard of living. Nearly 95 percent of all commercial energy produced in today's world is by fossil fuels. About 39 percent is coming from petroleum; next are coal, with 32 percent, and natural gas, with 24 percent. Nuclear power provides only about 2.5 percent of commercial energy worldwide. The supplies of petroleum and natural gas are running low, although these were not used in large quantities until the beginning of the 20th Century. Coal supplies may last several more centuries at current rates of uses. But it seems that the fossil fuel age is likely to be a rather short episode in the long history of mankind. The environmental damage caused by the burning of fossil fuels may necessitate cutting back on our use of these energy sources.
0 Lessons
Hours

 Compare
Compare
Soil pollution or contamination is largely caused by the presence of man-made chemicals or other alteration in the natural soil environment. This type of contamination typically arises from the failure caused by intensification of agriculture, irrigation methods, application of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, insecticides, percolation of contaminated surface water to subsurface strata, oil and fuel dumping, disposal of coal ash, leaching of wastes from landfills or direct discharge of industrial wastes to the soil, and corrosion of underground storage tanks (including piping used to transmit the contents). This chapter focuses attention on the importance of soil as natural resources, soil and land pollution, the classification and description of major soil pollutants, factors causing soil pollution, health and environmental impacts, and management.
0 Lessons
Hours

 Compare
Compare
Water is a major component of our natural environment. Everything we do by way of exploiting or managing it ((Chapter 7) has impacts on the environment. Analysis of the impacts of water pollution thus presents a formidable task and considerable challenge. Silt and sand are by far the major water pollutants in terms of quantity. Production of biomass by aquatic organisms, soil erosion, and refuge discharge all contribute to this problem. Addition of salts and metals from highway, farm runoff and industrial activities also damage water quality. Toxic chemical wastes have become an increasing water pollution problem in industrialized countries, Chemicals from agricultural fields and industrial units
0 Lessons
Hours