Courses

 Compare
Compare
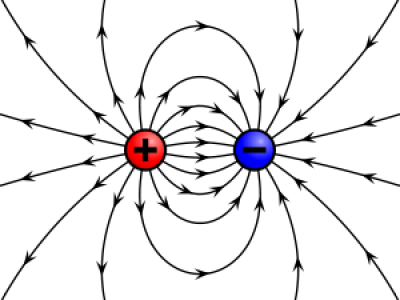
Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field.There are two types of electric charges; positive and negative (commonly carried by protons and electrons respectively).
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
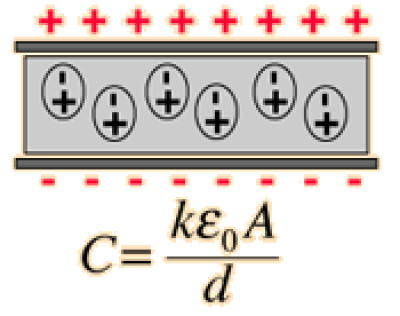
In the equations describing electric and magnetic fields and their propagation, three constants are normally used. One is the speed of light c, and the other two are the electric permittivity of free space ε0 and the magnetic permeability of free space, μ0. The magnetic permeability of free space is taken to have the exact value
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
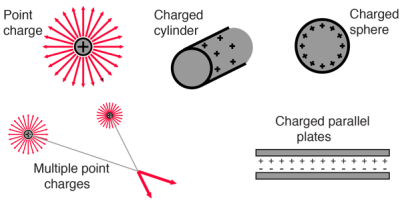
Electric field is defined as the electric force per unit charge. The direction of the field is taken to be the direction of the force it would exert on a positive test charge.
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
Consider a parallel plate capacitor that produces a uniform electric field between its large plates. This is accomplished by connecting each plate to one of the terminals of a power supply (such as a battery).
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
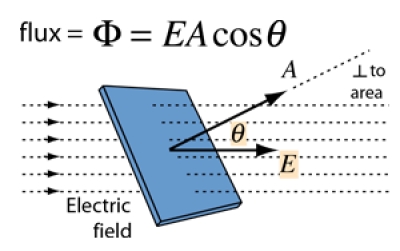
The electric flux through a planar area is defined as the electric field times the component of the area perpendicular to the field. If the area is not planar, then the evaluation of the flux generally requires an area integral since the angle will be continually changing
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
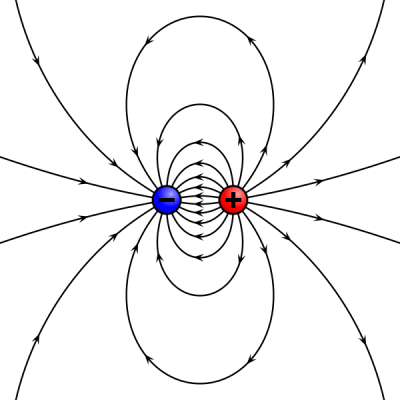
An electric dipole is a separation of positive and negative charges. The simplest example of this is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some (usually small) distance.
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
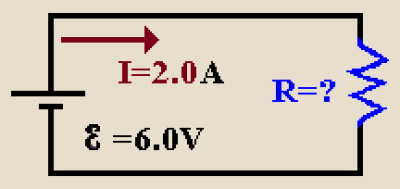
Ohm's Law states that: At a constant temperature the potential difference (voltage) across an ideal conductor is proportional to the current through it.
0 Lessons
Hours
 Compare
Compare
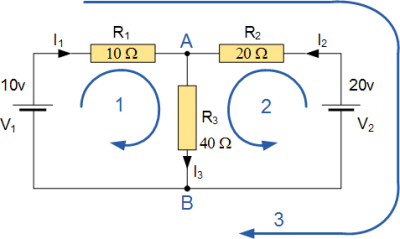
Circuit – a circuit is a closed loop conducting path in which an electrical current flows.
0 Lessons
Hours

 Compare
Compare
Faraday's law of induction is a basic law of electromagnetism predicting how a magnetic field will interact with an electric circuit to produce an electromotive force (EMF) — a phenomenon called electromagnetic induction.
0 Lessons
Hours