Course description
Electric Potential Energy (U) and Electric Potential (V):
Consider a parallel plate capacitor that produces a uniform electric field between its large plates. This is accomplished by connecting each plate to one of the terminals of a power supply (such as a battery).
Figure 1: An electric field is set up by the charged plates separated by a distance l. The charges on the plates are +Q and –Q.
Figure 2: An electric charge q is moved from point A towards point B with an external force T against the electric force qE.
Figure 3, 4: When it is moved through a distance d, its potential energy at the point B is qEd relative to the point A.
Figure 5: When released from B (T = 0), it will accelerate toward the lower plate. As it is moving toward the lower plate, its potential energy decreases and its Kinetic energy increases. When it reaches the lower plate (where we can choose the Potential energy to be zero), its potential energy at A is completely converted to Kinetic Energy :
Here qEd is the work done by the field as the charge moves under the force qE from B to A. Let m is the mass of the charge q, and v is its velocity as it reaches point A. Here we assumed that electric field is uniform. Work done by E field:
According to Kinetic Energy-Work theorem (Work Energy principle):
where we introduced the concept of potential energy and conservative force ( a force under which one can define a potential energy so that the work done only depends the differences of the potential energy function evaluated at the end points).
A rule of thumb for deciding whether or not EPE is increasing:
Ø If a charge is moving in the direction that it would normally move, its electric potential energy is decreasing.
Ø If a charge is moved in a direction opposite to that of it would normally move, its electric potential energy is increasing.
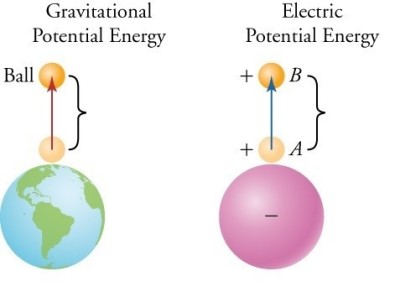
Ø This situation is similar to that of constant gravitational field (g = 9,8 m/s2).
Ø When you lift up an object, you are increasing its gravitational potential energy.
Ø Likewise, as you are lowering an object, its gravitational energy is decreasing.
Potential Difference
The work done by an E field as it act on a charge q to move it from point A to point B is defined as Electric Potential Difference between points A and B:
Clearly, the potential function V can be assigned to each point in the space surrounding a charge distribution (such as parallel plates).
The above formula provides a simple formula to calculate work done in moving a charge between two points where we know the value of the potential difference.
The above statements and the formula are valid regardless of the path through which the charge is moved.
A particular interest is the potential of a point-like charge Q. It can be found by simply performing the integration through a simple path (such as a straight line) from a point A whose distance from Q is r to infinity. Path is chosen along a radial line so that becomes simply Edr. Since the electric field of Q is kQ/r2,
This process defines the electric potential of a point-like charge. Note that potential function is a scalar quantity as oppose to electric field being a vector quantity.
q Suppose we compute the work done against electric forces in moving a charge q from infinity to a point a distance r from the charge Q. The work is given by:
Note that if q is negative, its sigh should be used in the equation. Therefore, a system consisting of a negative and a positive point-like charge has a negative potential energy.
A negative potential energy means that work must be done against the electric field in moving the charges apart.
Problem: System given below is composed of the charges, 10q, 8q and -5q. Find the total electric potential energy of the system.
Problem: Find the potential difference between points A and B, VAB in terms of kq/r?