Course description
Electric charge & Current:
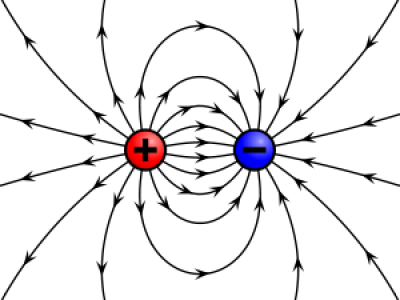
Ø Electric charge is the physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field.
Ø There are two types of electric charges; positive and negative (commonly carried by protons and electrons respectively).
Ø Like charges repel and unlike attract.
Ø An object with an absence of net charge is referred to as neutral.
Ø The SI derived unit of electric charge is the coulomb (C).
Ø The symbol Q often denotes charge
Electric charge is carried by subatomic particles. In ordinary matter, negative charge is carried by electrons, and positive charge is carried by the protons in the nuclei of atoms.
If there are more electrons than protons in a piece of matter, it will have a negative charge, if there are less it will have a positive charge, and if there are equal numbers it will be neutral.
Charge is quantized; it comes in integer multiples of individual small units called the elementary charge, e, about 1.602×10−19 coulombs, which is the smallest charge which can exist free. The proton has a charge of +e, and the electron has a charge of −e.
Electric charges create an electric field, if they are moving they also generate a magnetic field. The combination of the electric and magnetic field is called the electromagnetic field.
Electric Current
Ø An electric current is a flow of electric charge.
Ø In electric circuits this charge is often carried by moving electrons in a wire.
Ø It can also be carried by ions in an electrolyte, or by both ions and electrons such as in an ionised gas (plasma).
Ø The SI unit for measuring an electric current is the ampere, which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second.
Ø Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter.
Different Electrical Units
Volt (V)
Volt is the electrical unit of voltage.
One volt is the energy of 1 joule that is consumed when electric charge of 1 coulomb flows in the circuit.
1V = 1J / 1C
Ampere (A)
Ampere is the electrical unit of electrical current. It measures the amount of electrical charge that flows in an electrical circuit per 1 second.
1A = 1C / 1s
Ohm (Ω)
Ohm is the electrical unit of resistance.
1Ω = 1V / 1A
Watt (W)
Watt is the electrical unit of electric power. It measures the rate of consumed energy.
1W = 1J / 1s
1W = 1V ⋅ 1A
Farad (F)
Farad is the unit of capacitance. It represents the amount of electric charge in coulombs that is stored per 1 volt.
1F = 1C / 1V
Henry (H)
Henry is the unit of inductance.
1H = 1Wb / 1A
siemens (S)
siemens is the unit of conductance, which is the opposite of resistance.
1S = 1 / 1Ω
Coulomb (C)
Coulomb is the unit of electric charge.
1C = 6.238792×1018 electron charges
Ampere-hour (Ah)
Ampere-hour is a unit of electric charge.
One ampere-hour is the electric charge that flow in electrical circuit, when a current of 1 ampere is applied for 1 hour.
1Ah = 1A ⋅ 1hour
One ampere-hour is equal to 3600 coulombs.
1Ah = 3600C
Tesla (T)
Tesla is the unit of magnetic field.
1T = 1Wb / 1m2
Weber (Wb)
Weber is the unit of magnetic flux.
1Wb = 1V ⋅ 1s
Joule (J)
Joule is the unit of energy.
1J = 1 kg ⋅ m2 / s2
Kilowatt-hour (kWh)
Kilowatt-hour is a unit of energy.
1kWh = 1kW ⋅ 1h = 1000W ⋅ 1h
Kilovolt-amps (kVA)
Kilovolt-amps is a unit of power.
1kVA = 1kV ⋅ 1A = 1000 ⋅ 1V ⋅ 1A
Hertz (Hz)
Hertz is the unit of frequency. It measures the number of cycles per second.
1 Hz = 1 cycles / s
Units Prefix Table
Prefix
Prefix
Symbol
Prefix
factor
Example
pico
p
10-12
1pF = 10-12F
nano
n
10-9
1nF = 10-9F
micro
μ
10-6
1μA = 10-6A
milli
m
10-3
1mA = 10-3A
kilo
k
10 3
1kΩ = 1000Ω
mega
M
10 6
1MHz = 106Hz
giga
G
10 9
1GHz = 109Hz