Course description
The Israeli-American Relationship
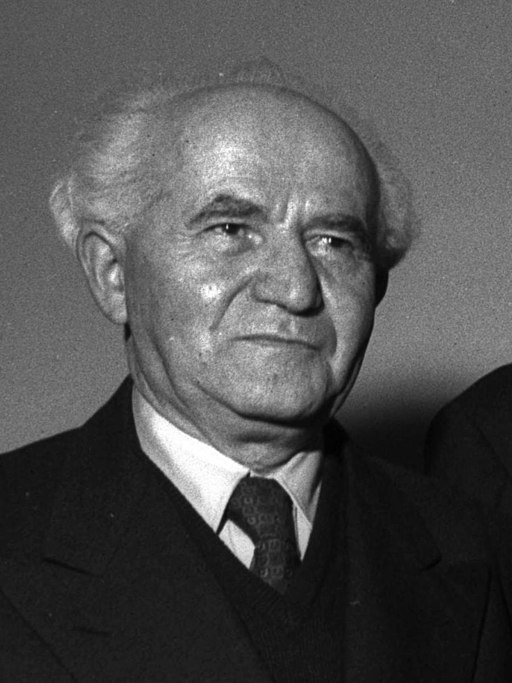 David Ben Gurion was the first person to proclaim a Jewish state in 2000 years on May 14, 1948. He was Chairman of the Jewish Agency, an organization established in 1929 with the aim to “ensure that every Jewish person feels an unbreakable bond to one another and to Israel no matter where they live in the world”. Ben Gurion also served as Israel’s first Prime Minister.
David Ben Gurion was the first person to proclaim a Jewish state in 2000 years on May 14, 1948. He was Chairman of the Jewish Agency, an organization established in 1929 with the aim to “ensure that every Jewish person feels an unbreakable bond to one another and to Israel no matter where they live in the world”. Ben Gurion also served as Israel’s first Prime Minister.
Immediately after the British withdrawal, fighting broke out between Arabs and Jews. Egypt also invaded Israel but, despite all that, the Jews celebrated the birth of their new nation, recognised first and foremost by the USA.
However, the idea of a free Jewish state was not born in Tel Aviv or Jerusalem, the modern and ancient capitals of the Jews. Its roots were planted long before as part of the Zionism movement in the Russian Empire. In 1896, a Jewish-Austrian journalist, Theodor Herzl, asked for a state to protect Jews from anti-Semitism. Palestine, the place chosen by the Jews for a homeland, was then controlled by the Ottomans (or Turkish sultans). This movement has ever since been called Zionism and is now linked to nationalist Israeli politics!
 After the Russian Revolution in 1917, eastern European and Russian Jews began to immigrate to Palestine where a few thousand had arrived before and insisted on using Hebrew, the ancient Jewish language used in their holy book, the Torah. During the First World War, the Ottomans lost Palestine to Britain. The Balfour Declaration, written by the British and named after the British Prime Minister of the time, shows a powerful interest in establishing a Jewish homeland in Palestine and was also accepted by the League of Nations, the ancestor of the United Nations, in 1922.
After the Russian Revolution in 1917, eastern European and Russian Jews began to immigrate to Palestine where a few thousand had arrived before and insisted on using Hebrew, the ancient Jewish language used in their holy book, the Torah. During the First World War, the Ottomans lost Palestine to Britain. The Balfour Declaration, written by the British and named after the British Prime Minister of the time, shows a powerful interest in establishing a Jewish homeland in Palestine and was also accepted by the League of Nations, the ancestor of the United Nations, in 1922.
Yet the British continued to rule over Palestine from 1920 to 1930 because of the Arabs’ opposition to a Jewish land there. After all, they were the people already living in the region. In 1929, Arabs and Jews started fighting openly in Palestine, so Britain had to limit Jewish immigration to pacify the Arabs.
As a result of the Holocaust, however, which caused the deaths of millions of Jews in Europe, many of them entered Palestine illegally during World War II. Radical Jewish groups thought the British were working against their interests and established several extremist terrorist groups. But six million Jews had been murdered by Hitler’s Nazis between the mid-1930s and the end of the Second World War in 1945 and there was huge sympathy for them. So, the USA took up the Zionist cause in the United Nations in a bid to partition Palestine but the organization was unable to find any practical solution. The Jews possessed more than half of the land there although they were far less than half of the population.
 The Palestinians fought them, backed by other Arab countries, but the Jews were able to get their UN-allocated land as well as some other Arab territory. On May 14, 1948, with the withdrawal of Britain’s troops, Israel was proclaimed a state. The next day, Arab countries including Egypt, Jordan, Syria, Lebanon and Iraq invaded Israel, but although the new state had less equipment and weapons, Israel not only managed to fight off the Arabs but also seized key territories, like Galilee, the Palestinian Coast, and the western section of Jerusalem.
The Palestinians fought them, backed by other Arab countries, but the Jews were able to get their UN-allocated land as well as some other Arab territory. On May 14, 1948, with the withdrawal of Britain’s troops, Israel was proclaimed a state. The next day, Arab countries including Egypt, Jordan, Syria, Lebanon and Iraq invaded Israel, but although the new state had less equipment and weapons, Israel not only managed to fight off the Arabs but also seized key territories, like Galilee, the Palestinian Coast, and the western section of Jerusalem.
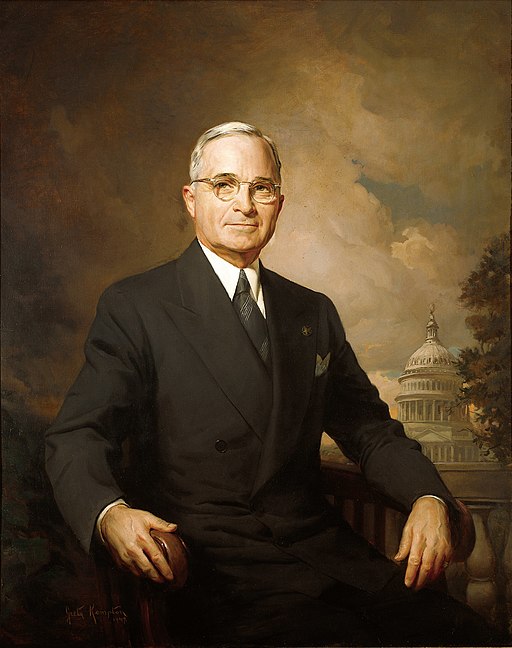
US President Harry Truman was the first world leader to recognize Israel. But even so, the new state did not always have good relations with the United States. There is evidence of this during the invasion of Egypt in 1956, when Israel seized part of Egypt's Sinai and Gaza and the United States threatened to cancel financial assistance. Israel’s secret nuclear project is another example of the USA going against the new state’s plans.
 But, after 1967, the relations between the United States and Israel began to grow closer. During the Arab-Israeli war in 1973, the Americans supported Israel. This decision guaranteed a strong relationship between the two countries. At that time, US presidents and diplomats realized that Israel could be an effective weapon in decreasing Soviet Russian influence in the Middle East.
But, after 1967, the relations between the United States and Israel began to grow closer. During the Arab-Israeli war in 1973, the Americans supported Israel. This decision guaranteed a strong relationship between the two countries. At that time, US presidents and diplomats realized that Israel could be an effective weapon in decreasing Soviet Russian influence in the Middle East.
After the Cold War, the United States was active in 'resolving' various conflicts and problems in the region. The main reason was to bring the oil market under their own control. Of course, a peaceful, stable region meant a continuous supply of oil, while fighting sent prices rocketing. So, the United States presented itself as the 'guarantor' of regional stability in the Middle East at that time.
Countries like Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Jordan, Egypt, and Israel agreed to this American ‘assistance’ because it allowed them to influence Middle Eastern politics. But others, such as Iran, Syria and Iraq, did not join hands with the US, which chose Israel to build military bases in the region to defend its interests there.
The United States then took on the responsibility of building bridges between Palestine and Israel, so that a lasting peace could be reached. Over the last few decades, every US president has tried to reconcile Israel with Palestine. However, American support for peace has always been more in favour of Tel Aviv.
 The United States does not support Israel only because of its foreign policy and Middle East strategy though. Israel has been a major issue in US domestic politics since the eighties because most Americans are sympathetic to the Israelis – about 70 % according to recent surveys. But why do US citizens support Israel? One of the major reasons is shared values of democracy and the Israeli liking for the European culture, fashion and way of life. Christian religious organizations are also strongly in favour of the Jewish state and Americans are, by and large, believers in the Christian faith. Perhaps ironically, there is some disagreement among Jews though. For example, 65% of America's Jews are against Israel's new settlements in the West Bank while Christians are positive about them. Again, Jews who are younger do not consider themselves as Zionists.
The United States does not support Israel only because of its foreign policy and Middle East strategy though. Israel has been a major issue in US domestic politics since the eighties because most Americans are sympathetic to the Israelis – about 70 % according to recent surveys. But why do US citizens support Israel? One of the major reasons is shared values of democracy and the Israeli liking for the European culture, fashion and way of life. Christian religious organizations are also strongly in favour of the Jewish state and Americans are, by and large, believers in the Christian faith. Perhaps ironically, there is some disagreement among Jews though. For example, 65% of America's Jews are against Israel's new settlements in the West Bank while Christians are positive about them. Again, Jews who are younger do not consider themselves as Zionists.
And then there is another factor: the American Israel Public Affairs Committee (AIPAC) with its aim of brining US and Israel always closer. Although AIPAC is not a political organization – or says it isn’t – it has a major impact on deciding US foreign policy. How does it manage this?
 AIPAC spends a lot of money on achieving its goals. It does not directly finance any party but supports its preferred candidates as individuals, especially Republicans. AIPAC has a special Congress Club, where each member gives a minimum of $5,000 every election. And this money is spent on helping pro-Israeli politicians. Of course, if the AIPAC candidates win seats in the Senate or Congress, they influence policies. Although it is not known how much money AIPAC spends overall, they do have members who give from one million dollars to hundreds of millions.
AIPAC spends a lot of money on achieving its goals. It does not directly finance any party but supports its preferred candidates as individuals, especially Republicans. AIPAC has a special Congress Club, where each member gives a minimum of $5,000 every election. And this money is spent on helping pro-Israeli politicians. Of course, if the AIPAC candidates win seats in the Senate or Congress, they influence policies. Although it is not known how much money AIPAC spends overall, they do have members who give from one million dollars to hundreds of millions.
 The relationship between the United States and Israel is also known as one of the most expensive in the world. Just as Israel spends a lot of money to make an impact in the United States, so does the United States in Israel. The United States signed a free trade agreement with Israel in 1985 and, ever since then, business between the two countries has increased considerably.
The relationship between the United States and Israel is also known as one of the most expensive in the world. Just as Israel spends a lot of money to make an impact in the United States, so does the United States in Israel. The United States signed a free trade agreement with Israel in 1985 and, ever since then, business between the two countries has increased considerably.
Of course, the million dollar question is if US support for Israel will continue forever. For instance, Barack Obama tried hard to stop Israeli settlements in the occupied West Bank and Gaza. His relationship with Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu was also very cold. However, Israel and AIPAC then put pressure on Obama through their close friends in Congress. And now Donald Trump has placed the US Embassy in Jerusalem, which both Palestinians and Jews want as a capital, a move that greatly angered the Arabs and America’s European allies, as well as its enemies,except, of course, Israel.
We will just have to wait and see what happens in the future.
If you want to watch some videos on this topic, you can click on the links to YouTube videos below.
If you want to answer questions on this article to test how much you understand, you can click on the green box: Finished Reading?
Videos :
1. Why Israelis and Palestinians both Claim Jerusalem (5:00)
2. The Israel-Palestine Conflict : a brief, simple History (10:18)
3. A brief History of the State of Israel (2:08)
4. How Israel becomes a Country (3:53)
5. The Cold War (5:53)
6. Information on the Holocaust (3:17)
7. U.S. - Israel Relations Explainer (2:48)
8. Trump's Relations with Israel and the American Jewish Community (3:12)